What is Anterior Placenta?
- Pregnancy
-
- UPDATED DECEMBER 08, 2024

by Tasha Mayberry
690 shares
The placenta is one of the crucial organs that helps women to have a healthy pregnancy, by supplying oxygen, immunity, essential hormones, and nutrients to the growing fetus from the mom’s blood supply. It also performs the job of taking out the waste produced by the fetus to the mom’s blood supply, so her body can get rid of the same. But, it is a topic that not many women are aware of or try to gain knowledge about. As a result, when they find out that they have an anterior placenta, they are often confused about what to expect.
Anterior Placenta
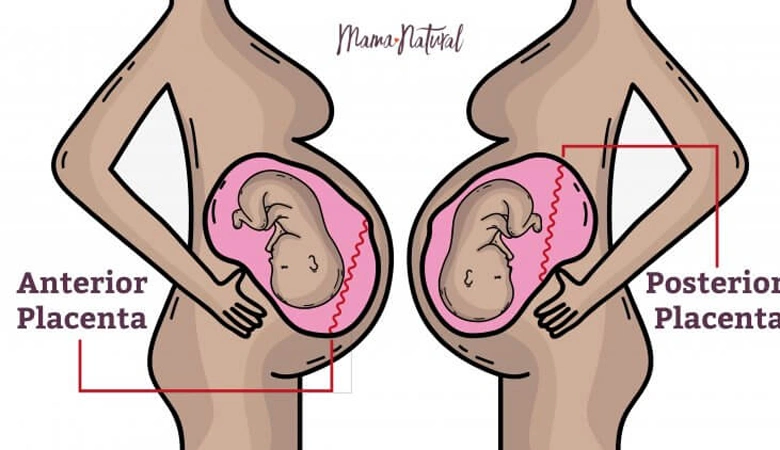
Usually taking place during the first few weeks of pregnancy, an anterior placenta happens when your placenta attaches itself to the front wall of your uterus. In general, the placenta attaches itself in different positions, as follows:
● Anterior – attached to the front wall of the uterus
● Posterior – attached to the back wall of the uterus
● Fundal – attached on the top wall of the uterus
● On the right or left side of the uterus
● Low-lying – attached at the bottom of the uterus
In most cases, a fertilized egg gets implanted on the back of the uterus wall, after which the placenta also forms along the same wall, and it is widely referred to as the posterior placenta. In the case of an anterior placenta, the placenta will form between the fetus and the front of your stomach.
Diagnosis

You can find out about the positioning of your placenta during your 20-week ultrasound, also known as your anomaly scan. Sometimes, if you are asked to take a scan earlier, say about 18 weeks, you could diagnose the position of your placenta sooner. But, know that this will not be the permanent position of your placenta, because it could move to the sides, back, or top of your uterus wall as your uterus grows and stretches.
Effects of an Anterior Placenta
Generally, the position of your placenta doesn’t make any difference or affect your pregnancy in any way, unless it blocks the cervix, simply because your little one doesn’t really care where he/she is lying inside your uterus.Even with its anterior positioning, your placenta will still do its job of nourishing your child;
but, there are a few things you should expect:
Baby’s Movements

Pregnant women tend to start feeling their baby’s kicks or movements as early as 18 weeks, and sometimes sooner, which usually happens in women who have already given birth because their body would already be ready and they know how the movements feel like. For women who are pregnant for the first time and those with an anterior placenta, this can take even up to 24 weeks. Since an anterior placenta acts as an additional layer between your stomach’s outer wall and your baby, there will an extra level of cushioning, which makes it more difficult for you to feel your baby’s movements. As a result, you may have to wait a little longer, until your little one is big enough to make his/her kicks and movements more prominent.
Though you may have to try a lot more to feel your baby’s movements, you should be able to feel them nevertheless. You should contact your doctor if you are over 24 weeks pregnant and still have not felt your baby kick or move, you know that the movements have significantly reduced than usual, and you don’t feel any movement even after trying to track
the same for more than a couple of hours.
Screening Tests

Having an anterior placenta can make it difficult to perform certain screening tests, like amniocentesis, which is a prenatal test that looks at your amniotic fluid. This test will be recommended only to those women whose screening tests show high certainty of their baby having conditions like Down’s syndrome, etc. In the test, a needle will be inserted into the women’s abdomen to obtain a sample from her amniotic sac for testing. Having an anterior placenta can make this process difficult; however, a medical professional will know ways to bypass the difficulty.
Hearing the Baby’s Heartbeat
During your prenatal tests, a fetal doppler will be used by your doctor to listen to your baby’s heartbeat. When you have an anterior placenta, your baby will be positioned behind the placenta, and this can make it difficult to find and listen to his/her heartbeat, which means it could take longer for your doctor to find the same.
Possible Complications
Having an anterior placenta doesn’t really cause complications during pregnancy or delivery, except for when the placenta moves down at some point in time and blocks the cervix, which is when you could experience complications like heavy bleeding. Otherwise, you could expect to have some of the usual complications that all pregnant women experience during some stage of their pregnancy, except that you are more likely to experience them due to your
condition. These complications are:
● C-section
● Increased hypertension
● Placenta previa (low-lying placenta)
● Induction of labor
● Longer labor
● Gestational diabetes
● Placental abruption – a condition when a part of or the whole placenta unexpectedly
gets separated from the uterus
Seeing Your Doctor

While you will visit your doctor on a regular basis for physical exams, with an anterior placenta, you should call to see your doctor immediately if you experience the following symptoms:
● Severe back pain
● Vaginal bleeding
● Severe pain in the stomach
● Sudden and frequent contractions
● Reduced fetal movement
● Tightening feeling in the abdomen or uterus
Of course, complications are rare with an anterior placenta, but it will give you peace of mind to make sure that everything is fine with you and your little one by having regular check-ups.